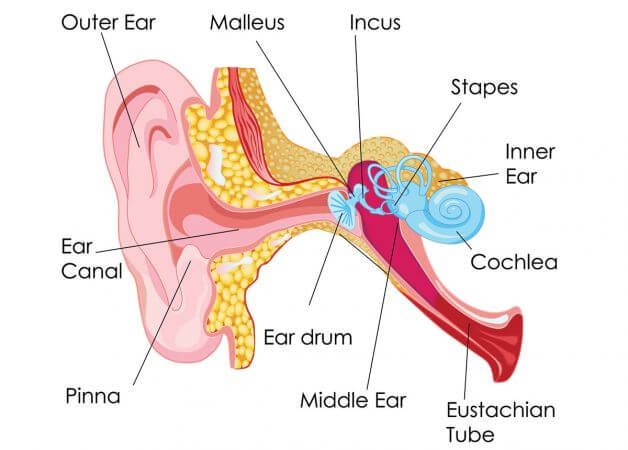
The auditory system is relatively simple compared to other senses; This is because the process by which
sound vibrations are converted into nerve impulses has a linear character. The sound is transmitted
from the ear to the auditory nerve, and from it to the brain, by a chain of internal structures.
In this article we will describe the outer, middle and inner ear, the main components of the auditory
system, as well as the substructures that make up each of these sections. To complete this description
we will explain the process by which the vibrations of the air become sounds perceptible to humans.
Parts of the outer ear: from the ear to the eardrum
The outer ear is composed of the ear, the ear canal and the eardrum or tympanic membrane. The
function of this segment of the auditory system is to capture the sound vibrations and channel them
towards the innermost parts of the ear. In this process some of the frequencies collected are increased
and others reduced, so that the sound is modified.
1. Ear or ear pin
The ear is the outermost component of the auditory system, and the only one that can be seen from the
outside. This structure, also known as the "auricular pavilion", is composed of cartilage and skin. Its
function is to collect the auditory energy and redirect it to the middle ear through the ear canal.
2. Auditory channel
The auditory canal is a cavity that connects the ear to the eardrum. The sound vibrations reach the
middle ear through this channel, which is approximately 2.5 to 3 centimeters long and only 7 square
millimeters in diameter.
3. Tympanic membrane or tympanic membrane
The eardrum is a membrane that separates the outer ear and the middle ear; Strictly speaking, it is not
part of any of these segments, but rather it is the structure that is used to delimit them. It is also known
as "tympanic membrane".
Middle ear: the chain of ossicles
After reaching the eardrum, the sound vibrations are transmitted through the ossicles of the middle ear
to the oval window of the cochlea, where transduction will be carried out in nerve impulses.
1. Hammer, anvil and stirrup
The chain of ossicles is formed by the hammer, the anvil and the abutment. Amphibians, reptiles and
birds have only one bone, the columella, which is morphologically equivalent to the stapes of mammals.
The hammer is attached to the eardrum, while the abutment connects to the cochlea; the transmission
of vibrations by the ossicles causes the lymphatic fluid of the inner ear to move, a necessary step for the
transduction of sound.
2. Oval window
The oval window is the membrane that covers the cochlea, so it is technically located between the inner
ear and the middle. The vibrations in the eardrum are transmitted through the ossicles to the oval
window, which consequently also vibrates, stimulating the inner ear.
Inner ear: the cochlea and transduction
The inner ear is a cavity that is located inside the skull. This is where the transduction of sound
vibrations in nerve impulses is carried out, which marks the beginning of the auditory brain processing.
The key structure of the inner ear is the cochlea, a set of channels that rotate on themselves and amplify
the auditory signals they receive. Within the cochlea is the organ of Corti, responsible for the hearing.
1. Semicircular canals
The semicircular canals or ducts are an organ of the inner ear composed of two compartments, which
allow the sense of balance in association with the chain of ossicles.
2. Vestibular or superior scale
The oval window of the cochlea, which is located in the vestibular scale, connects the abutment with the
rest of the inner ear. This structure is filled with perilymph, a substance similar to the cerebrospinal fluid
that receives the vibrations of the ossicular chain.
3. Tympanic scale or lower
The sound waves received by the upper scale are transmitted to the lower one through the perilymph
since the two structures are connected by this fluid, while the basilar membrane separates them.
4. Cochlear or average scale
The cochlear scale is isolated from the vestibular and tympanic scars by Reissner's membrane and
basilar membrane, respectively; however, it also shares endolymph with other parts of the inner ear.
In the middle scale, the organ of Corti is located, where the transduction of the sound vibrations in
neural impulses is carried out. The hair cells that are in this structure allow transduction.
5. Auditory or vestibule cochlear nerve
The vestibule cochlear or auditory nerve, composed in turn by the cochlear and vestibular nerves,
transmits information about sound and balance from the inner ear to the central nervous system. The
vestibule cochlear nerves constitute the eighth of the twelve cranial nerves.
Are you looking for ear wax removal?
Our clinic based service in Barnard Castle carries out microsuction ear wax removal. To find out more please view our Barnard Castle Clinic.
You can book an appointment online or call our Barnard Castle service at 01833 200 029.
Our clinic based service in Stockton-on-Tees carries out microsuction ear wax removal. To find out more please view our Stockton-on-Tees Clinic.
You can book an appointment online or call our Stockton-on-Tees service at 01833 200 029.
Our clinic based service in Bristol carries out microsuction ear wax removal. To find out more please view our Portishead Clinic.
You can book an appointment online or call our Bristol service at 01934 314 104.
Find a professional ear wax removal clinic around you !
Are your ears blocked? Browse our UK's network
of ear wax removal clinics
Our clinic based service in Bristol carries out microsuction ear wax removal. To find out more please view our Shirehampton Clinic.
You can book an appointment online or call our Bristol service at 01934 314 104.
Our clinic based service in Ruislip carries out microsuction ear wax removal. To find out more please view our Ruislip Clinic.
You can book an appointment online or call our Ruislip service at 020 3828 7705.
Our clinic based service in Wembley carries out microsuction ear wax removal. To find out more please view our VIP Hearing Solutions - Wembley.
You can book an appointment online or call our Wembley service at 020 3828 7705.